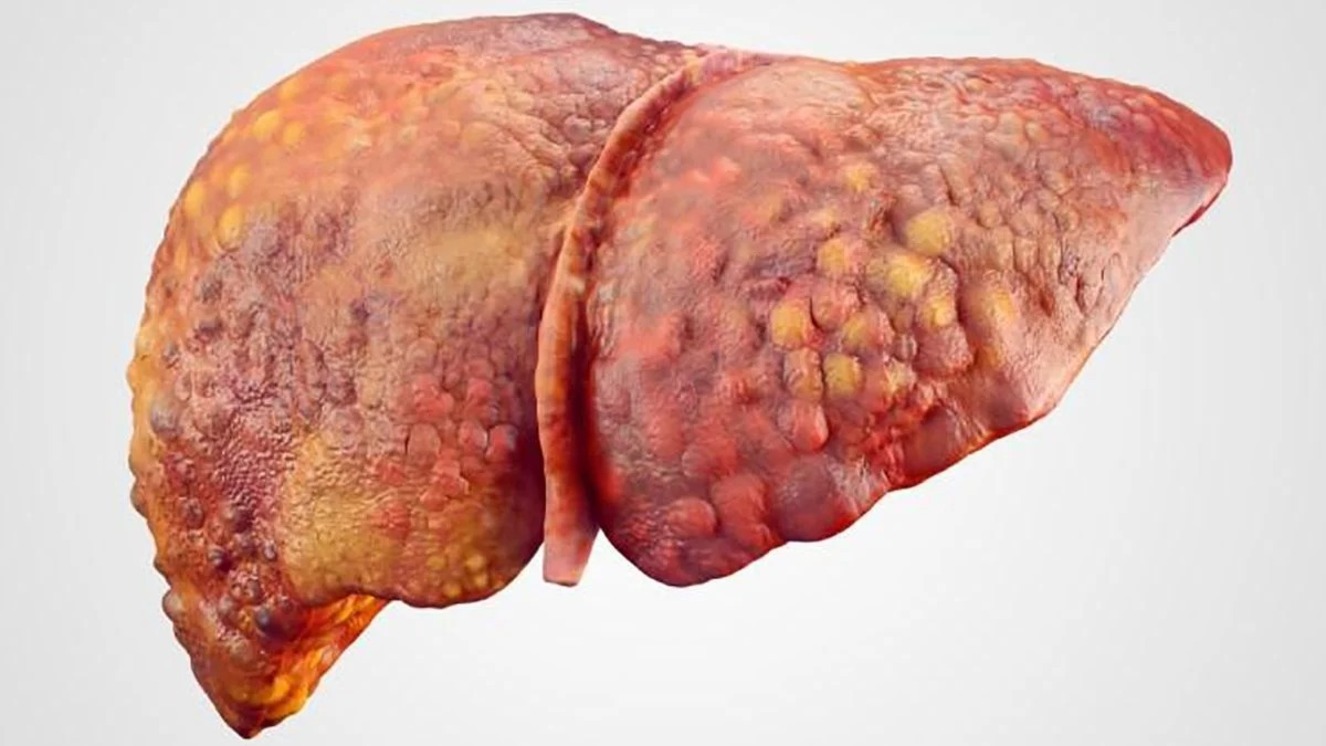
Increase in Cirrhosis Due to Increased Alcohol Consumption
In 2024, the United States has experienced a concerning increase in cases of hepatic cirrhosis, a chronic liver disease that can lead to liver failure and, in severe cases, death. This rise is closely linked to increased alcohol consumption, particularly among young and adult populations.
Relationship Between Alcohol Consumption and Hepatic Cirrhosis
Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption is one of the leading causes of hepatic cirrhosis. Studies have shown that consuming between 36 and 48 grams of alcohol per day increases the risk of developing cirrhosis fivefold in men and tenfold in women.
Moreover, factors such as body mass index (BMI) can influence susceptibility to alcohol-related liver damage; individuals with higher BMI levels are at greater risk of developing cirrhosis compared to those with lower.
Recent Statistics
Recent data indicate a significant rise in cases of alcohol-related liver diseases. For example, in Chihuahua, Mexico, a 12.5% increase in cases of alcoholic liver disease was reported between January and October 2023, compared to the same period in 2024, rising from 279 to 314 cases.
This pattern is reflected across various regions, highlighting a concerning global trend.
Contributing Factors
Several factors have contributed to the rise in alcohol consumption and, consequently, in cirrhosis cases:
Normalization of Alcohol Consumption: The societal perception of alcohol consumption as an acceptable and common activity has led to increased intake, even at younger ages.
Accessibility and Availability: The easy availability and low cost of alcoholic beverages facilitate excessive consumption.
Lack of Awareness of Risks: Many individuals are unaware of the risks associated with excessive alcohol consumption, including the potential development of hepatic cirrhosis and other severe health issues.
Preventive Measures and Recommendations
To address this public health issue, it is essential to implement prevention and awareness strategies:
Education and Awareness: Inform the population about the risks of excessive alcohol consumption and its consequences for liver health.
Regulations and Public Policies: Implement policies that limit alcohol availability, particularly to minors, and promote responsible consumption.
Early Intervention Programs: Provide support and treatment to individuals with risky alcohol consumption patterns to prevent the development of cirrhosis and other liver diseases.
Conclusion
The increase in hepatic cirrhosis cases linked to rising alcohol consumption is a public health concern requiring immediate attention. Implementing preventive measures, along with education and awareness among the population, is essential to reverse this trend and protect the liver health of future generations.







DEJE UN COMENTARIO:
¡Únete a la discusión! Deja un comentario.