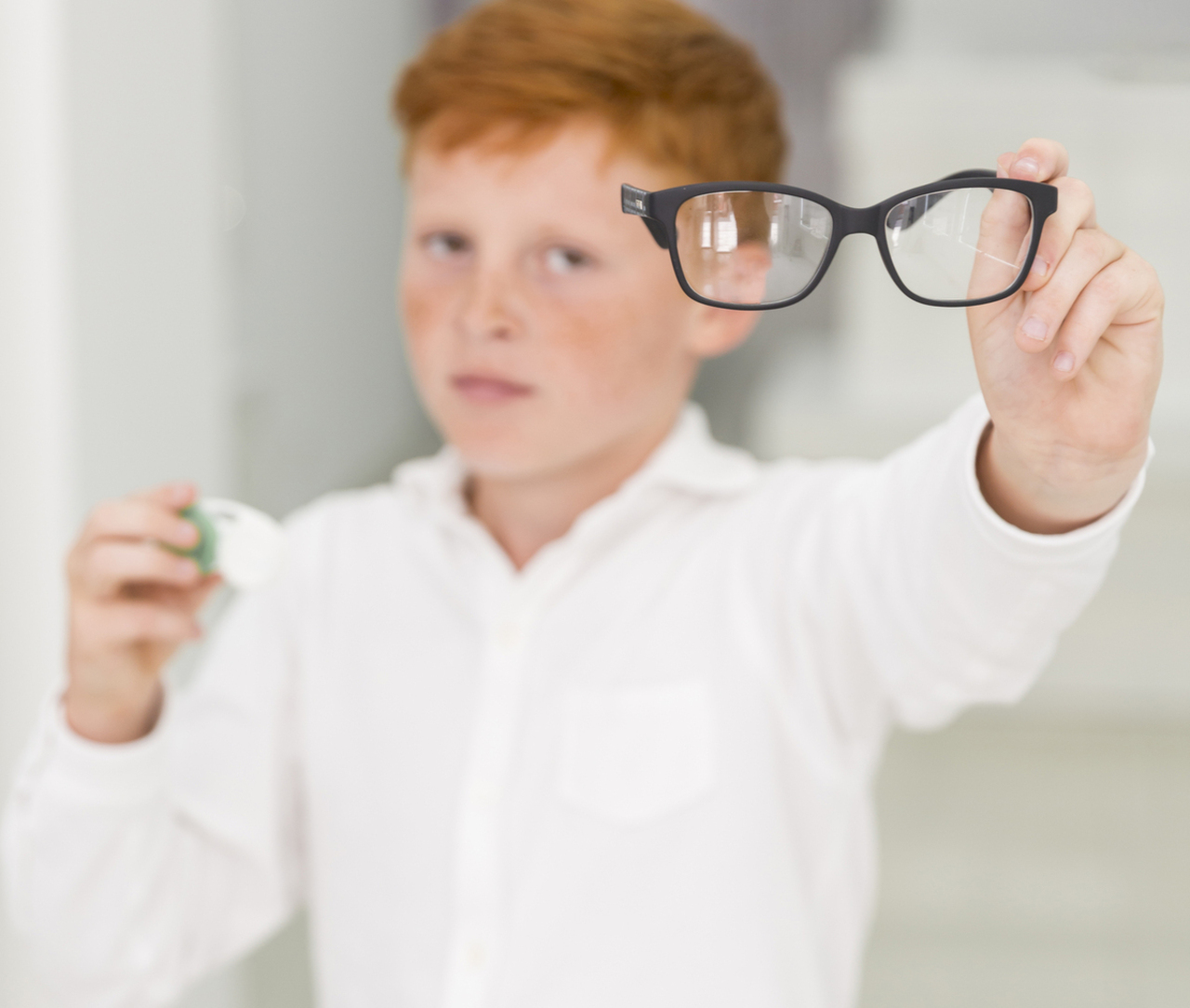

Myopia on the Rise Among Children and Adolescents Worldwide
The increasing prevalence of myopia among children and adolescents is a global concern that requires the implementation of preventive strategies.
Global Myopia Crisis: 1 in 3 Children is Nearsighted
Myopia, a vision condition that makes it difficult to see distant objects, is increasing at an alarming rate worldwide, especially among children and adolescents. Currently, it is estimated that more than one-third of young people worldwide suffer from myopia, and projections indicate that this number could reach 40% by 2050, affecting over 740 million children aged 5 to 19 years.
Factors Contributing to the Rise of Myopia
Various studies indicate that modern lifestyle habits play a crucial role in the rise of childhood myopia. The increased use of digital devices and reduced time spent outdoors are significant factors. Lack of exposure to natural light and prolonged focus on near objects, such as screens and books, contribute to both the development and progression of myopia.
Future Projections and Regional Challenges
Projections indicate that myopia rates will be highest in Asia, with an estimated 69% prevalence by 2050. Additionally, girls and young women are expected to have a higher incidence than boys. This increase presents a significant challenge for global public health systems, as uncorrected or progressive myopia can lead to severe eye complications in adulthood.
Strategies for Prevention and Control
To combat this growing trend, experts recommend promoting healthy vision habits from an early age. Suggested strategies include:
- Increased Outdoor Time: Experts recommend that children spend at least two hours daily outdoors, as exposure to natural light promotes healthy eye development.
- Limiting Screen Time: Reducing the amount of time spent on digital devices and encouraging regular breaks from near-focus activities may help slow myopia progression.
- Regular Eye Exams: Routine ophthalmological check-ups allow for early detection and proper management of myopia, preventing future complications.
Conclusion
The rising prevalence of myopia among children and adolescents is a global concern that requires preventive and educational measures. Encouraging healthier lifestyles, including more outdoor activity and less screen time, is crucial to addressing this emerging vision crisis and protecting the eye health of future generations.








LEAVE A COMMENT: