3D Bioprinting of Human Tissues: Fast and Highly Precise
3D bioprinting has emerged as a revolution in modern medicine, enabling the creation of human tissues with unmatched precision and speed.
3D Bioprinter Creates Human Tissue Structures in Seconds
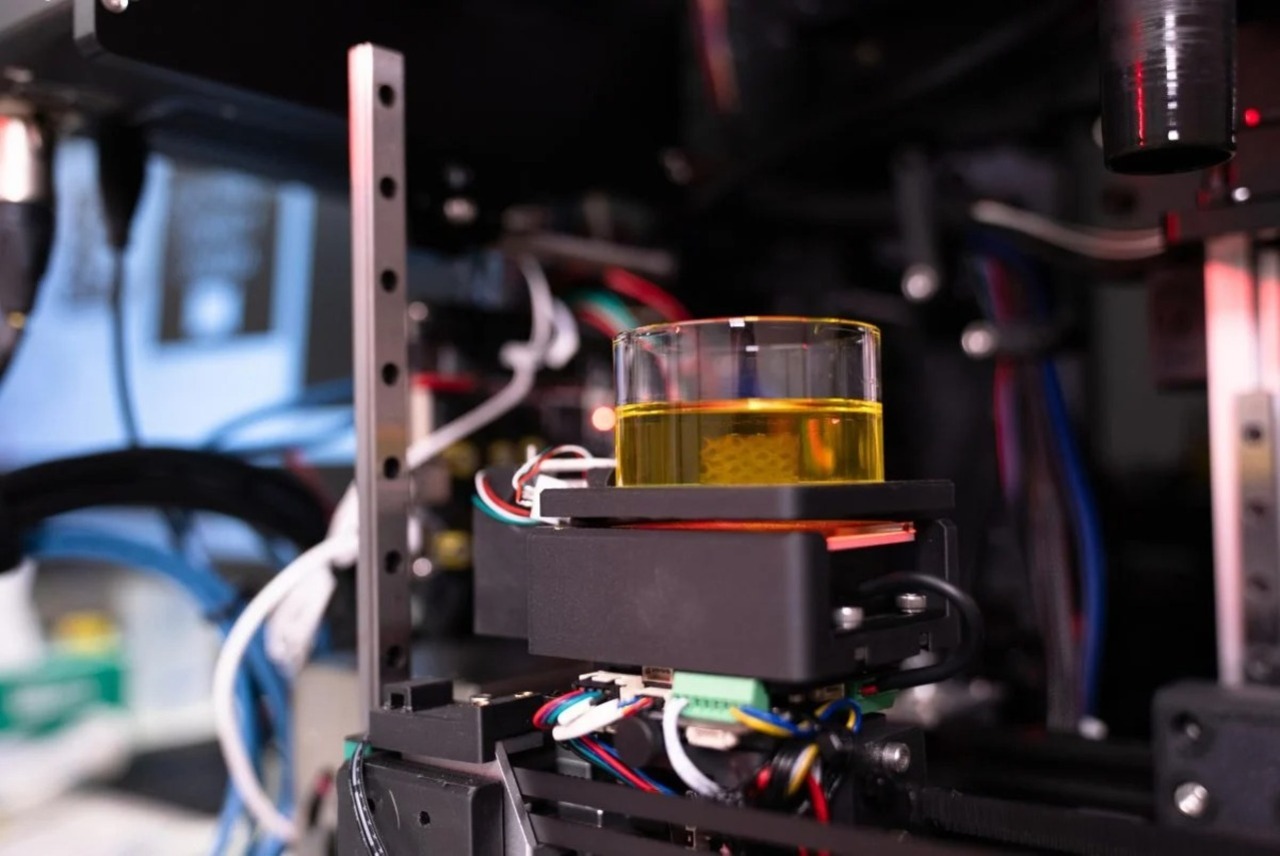
3D bioprinting has emerged as a revolution in modern medicine, enabling the creation of human tissues with unprecedented precision and speed. Biomedical engineers from the University of Melbourne have developed a 3D bioprinter capable of fabricating structures that closely mimic various human tissues, from muscles to bones.
Innovation in 3D Bioprinting
The technology developed by the University of Melbourne team stands out for its ability to print complex cellular structures within seconds, surpassing the limitations of traditional methods, which are often slower and less precise. This efficiency and speed open new possibilities in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Applications in Drug Testing
One of the most promising applications of this technology is its potential to test drugs without relying on animal experimentation. By accurately replicating human tissues, researchers can evaluate the effectiveness and safety of new medications in models that better represent the human body. This not only improves the relevance of the results but also addresses ethical concerns regarding the use of animals in research.
Challenges and the Future of Bioprinting
While these advancements are significant, 3D bioprinting still faces challenges, such as replicating complex vascular systems and integrating printed tissues into the human body. However, with interdisciplinary collaboration and increased research investment, it is likely that these barriers will be overcome in the near future, making 3D bioprinting a standard tool in personalized medicine and pharmaceutical research.
Conclusion
3D bioprinting represents an exciting frontier in biomedicine, with the potential to transform how medical treatments are developed and tested. The ability to create human tissues in seconds not only accelerates research but also promises more ethical and effective solutions in healthcare.










LEAVE A COMMENT: