How the world is doing on nuclear weapons
While France points to the need to strengthen nuclear weapons defense capabilities, the world worries about an escalation of nuclear weapons.
In a geopolitical context marked by growing tensions and conflicts in different parts of the world, nuclear weapons are once again the subject of international debate. France has recently expressed the need to strengthen its nuclear deterrent, reviving fears of a new arms race. However, data indicate that the number of nuclear warheads in the world remains alarming.
As reported by AFP, French President Emmanuel Macron said last week he wanted to open a debate on extending France's nuclear deterrent to other European nations as security risks increase following Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
"I have decided to open the strategic debate on protecting our allies on the European continent through our nuclear deterrent," he said in a televised address to the nation, in response to comments by Germany's likely next chancellor, Friedrich Merz, on extending the nuclear umbrella, adding that any decision on the use of nuclear weapons would be left to the French head of state.
An existing arsenal
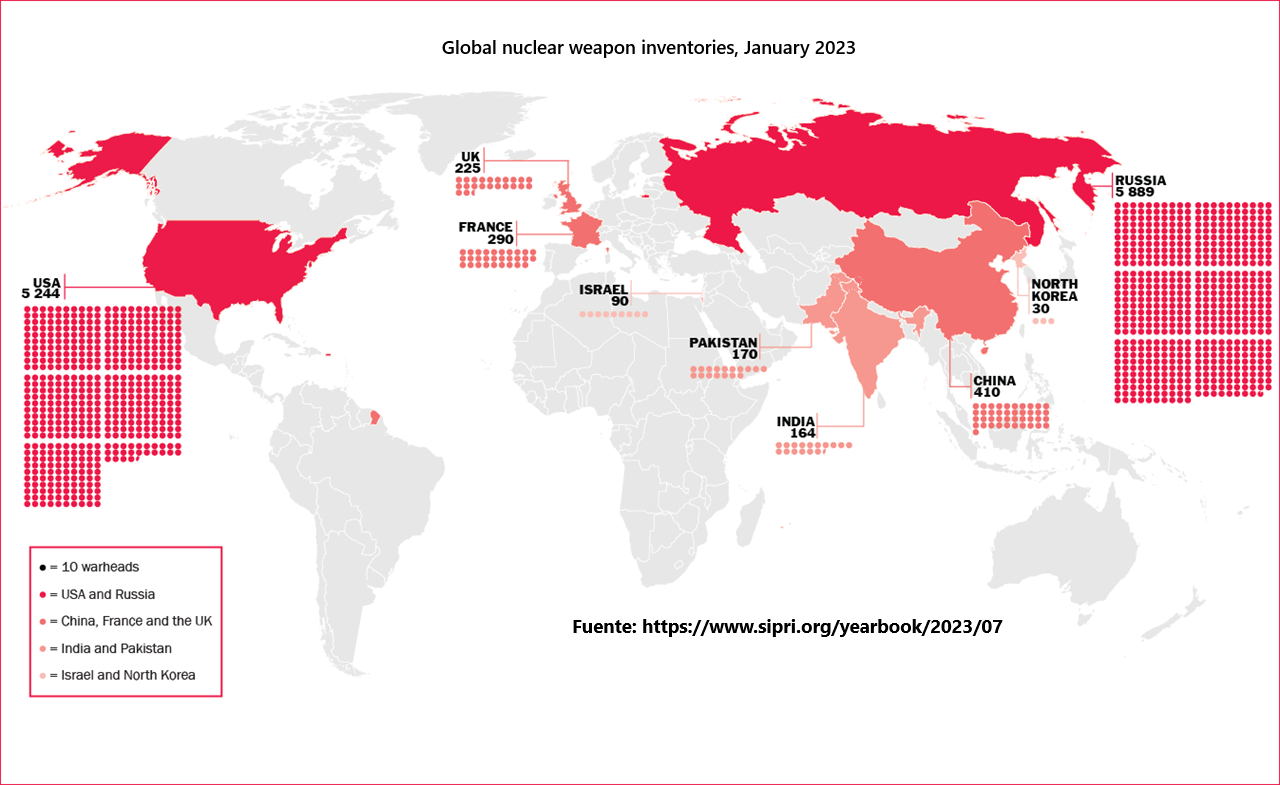
According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), there are currently around 12,500 nuclear weapons in the world, with Russia and the United States possessing approximately 90% of this arsenal. These two countries maintain their position as the leading nuclear powers, with Russia possessing 5,889 warheads and the United States 5,244, according to data from the Federation of American Scientists (FAS).
China, for its part, has increased its arsenal to 410 nuclear warheads, a figure that, according to projections by the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, could double in the next 20 years. In Europe, France maintains approximately 290 nuclear weapons, while the United Kingdom has 225 warheads, with plans to expand its nuclear capacity in the coming years.
Beyond the traditional powers, other nations have also developed nuclear arsenals. India and Pakistan maintain between 160 and 180 warheads each, while Israel - without officially recognizing its nuclear capability - is estimated to possess between 80 and 90 warheads, according to SIPRI.
One of the most worrying cases is that of North Korea, which has stepped up its nuclear program in recent years. According to the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, Kim Jong-un's regime may have between 30 and 40 nuclear weapons, with the capacity to further increase its arsenal through testing and new delivery technologies.
RELATED CONTENT
The global dilemma
French President Emmanuel Macron's statements on the need to strengthen nuclear deterrence have generated mixed reactions in Europe. While some countries see this as a security guarantee against threats such as the war in Ukraine, others warn that it could fuel a new arms race.
According to SIPRI, the modernization of nuclear arsenals has become a common trend among major powers, suggesting that instead of moving towards disarmament, the world is entering a new era of nuclear proliferation. The United States, Russia and China have allocated budgets in the millions to improve their nuclear capabilities, including the development of hypersonic missiles and advanced defense systems.
Despite the efforts of international organizations and treaties such as the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), the reality shows that disarmament remains a distant challenge. While some countries seek to strengthen their security with nuclear weapons, the fear of military escalation and possible confrontation remains latent.
The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists has warned that the world is closer than ever to a nuclear catastrophe, symbolically represented by its Doomsday Clock, which in 2024 marked 90 seconds to midnight, the most critical position in history.
Against this backdrop, the challenge for the international community is to find a balance between security and diplomacy, preventing fear and mistrust from driving the world to a point of no return.










LEAVE A COMMENT: