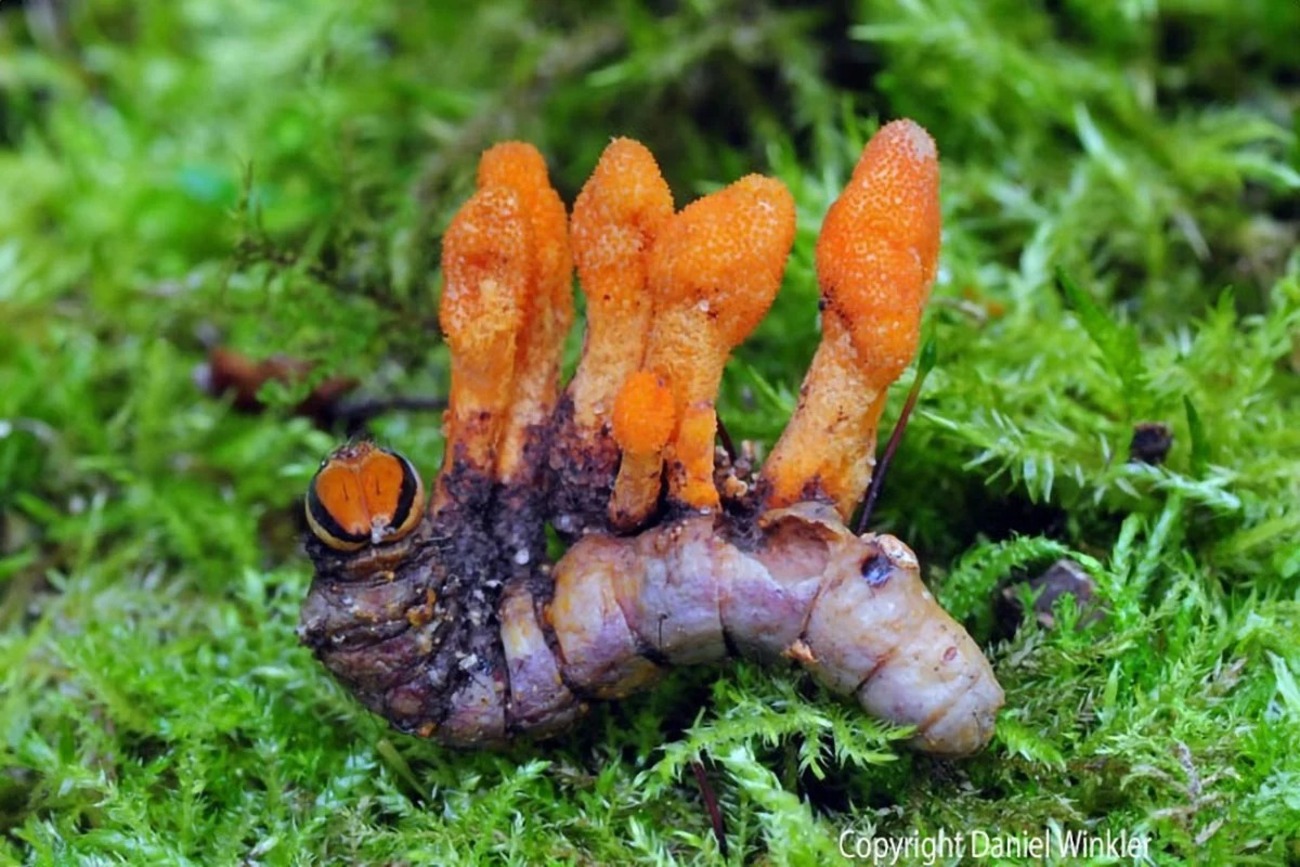

The Fight Against Cancer with Caterpillar Fungus
esearchers at the University of Oxford, in collaboration with the biopharmaceutical company NuCana, have developed an experimental drug called NUC-7738, derived from the caterpillar fungus (Ophiocordyceps sinensis), traditionally used in Chinese medicine for its therapeutic properties. This fungus contains cordycepin, a compound with anticancer potential; however, it degrades quickly in the bloodstream, limiting its effectiveness.
To overcome this limitation, scientists used ProTide technology, allowing NUC-7738 to enter cancer cells more efficiently and resist degradation in the blood. In vitro studies have shown that NUC-7738 is up to 40 times more potent than natural cordycepin in destroying cancer cells.
The mechanism of action of NUC-7738 involves altering cell growth signals at the genetic level, inhibiting tumor cell proliferation. Phase 1 clinical trials are currently underway to assess its safety and efficacy in patients with advanced solid tumors. Preliminary results are encouraging, showing antitumor activity and acceptable tolerance by patients.
This breakthrough represents a promising step toward developing new cancer treatments based on modified natural compounds, potentially offering more effective therapies with fewer side effects for patients.









DEJE UN COMENTARIO:
¡Únete a la discusión! Deja un comentario.