
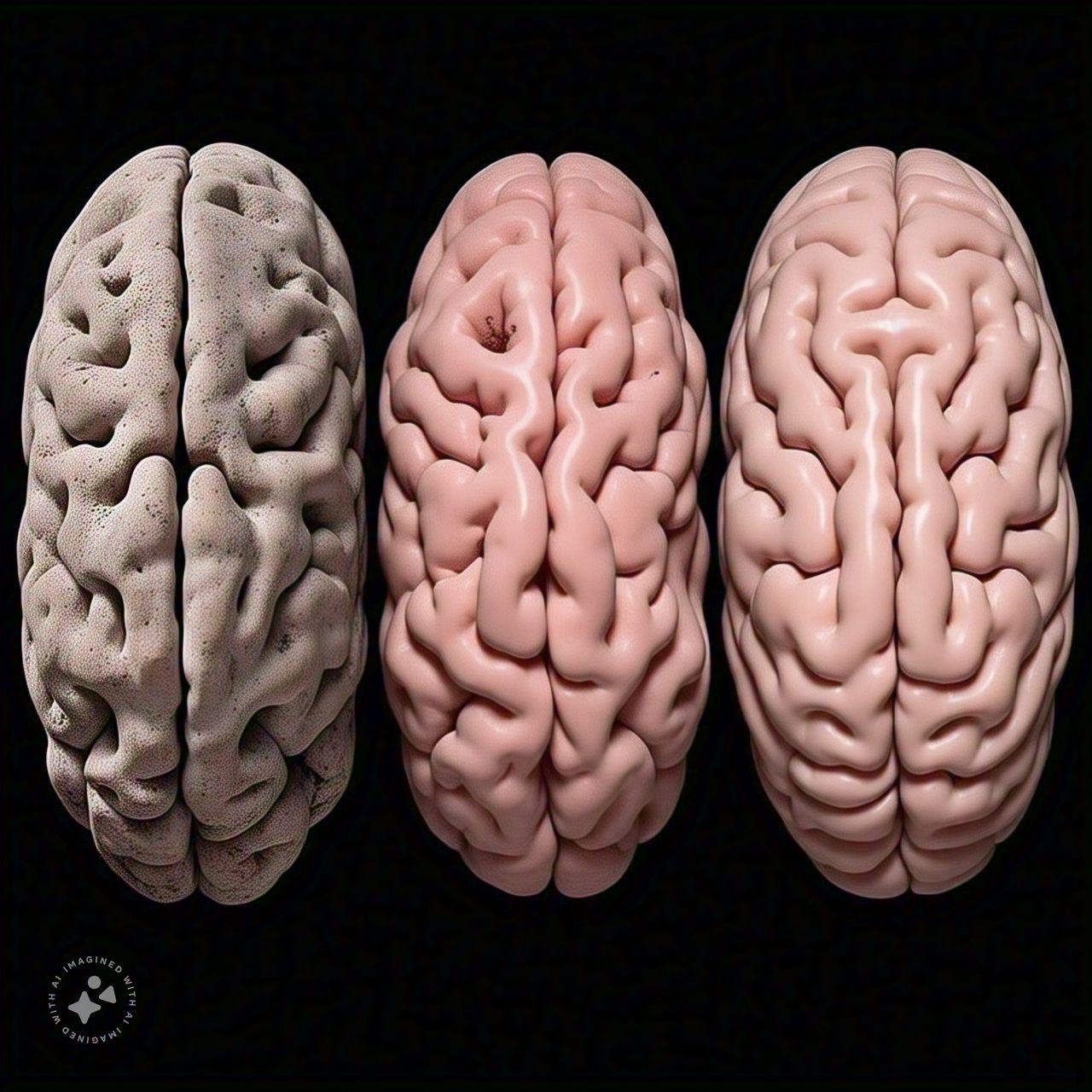
Cannabis Use Shrinks the Brain
Recent research has revealed that cannabis consumption among young Americans is associated with structural changes in the brain, including potential reductions in brain volume and alterations in neural connectivity. These effects are attributed to the high concentrations of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) present in commercial cannabis products, which have significantly increased in recent decades.
Effects of THC on the Adolescent Brain
THC, the primary psychoactive component of cannabis, interacts with the brain's endocannabinoid system, which plays a crucial role in neural development, especially during adolescence. During this stage, the brain undergoes maturation processes such as synaptic pruning and myelination, which are essential for cognitive and emotional development. Exposure to THC can interfere with these processes, leading to alterations in areas such as the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for executive functions and impulse control. Studies have shown that regular cannabis use in adolescents is associated with accelerated thinning of the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, potentially affecting decision-making and impulsive behavior.
Increased Potency of Cannabis and Its Implications
In recent decades, the concentration of THC in cannabis products has increased significantly. In the 1980s, the average THC content was approximately 1%, while in 2018, it reached around 20% in Canada. This increase in cannabis potency amplifies the risks associated with its use, particularly in developing brains. Higher THC concentrations can intensify psychoactive effects and increase the likelihood of developing psychiatric disorders, such as psychosis and schizophrenia, in young consumers.
Cognitive and Emotional Consequences
Cannabis use during adolescence has been linked to deficits in cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and learning. Additionally, there is a higher incidence of mood disorders, including depression and anxiety, among young consumers. These effects can have long-term repercussions, affecting academic performance and quality of life in adulthood.
Need for Awareness and Prevention
Given the increasing availability and social acceptance of cannabis, it is crucial to implement education and prevention programs targeted at young people and their families. Informing about the risks associated with cannabis use, especially products with high THC concentrations, is essential to mitigate negative effects on brain health and cognitive development in younger generations.
In conclusion, scientific evidence highlights the importance of addressing cannabis use among youth as a public health issue, promoting policies and strategies that protect brain development and the well-being of young individuals.









DEJE UN COMENTARIO:
¡Únete a la discusión! Deja un comentario.